Amoxicillin and Tylenol: Safe Use for UTI, Dental Pain, and More
When you're dealing with infections or pain, it's common to be prescribed medications like amoxicillin and Tylenol. Amoxicillin is a powerful antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections, while Tylenol, also known as acetaminophen, is a widely trusted over-the-counter pain reliever. Many people wonder about the safety of using both together, especially when managing conditions like a dental infection, urinary tract infection (UTI), or even general fever. That’s where the question often comes up: can you take Tylenol with antibiotics?

Understanding how Tylenol and amoxicillin work separately—and together—is important for effective and safe relief. While amoxicillin and Tylenol target different symptoms, combining them can be beneficial in cases where you're dealing with pain and infection simultaneously. If you’ve ever searched “can you take Tylenol with antibiotics” after a doctor's visit, you’re not alone. Proper knowledge helps avoid overmedication or harmful interactions, especially in sensitive situations like pregnancy or chronic conditions.

Whether you're managing a painful UTI, a throbbing toothache, or seeking safer options during pregnancy, knowing when and how to use amoxicillin and Tylenol matters. In this blog, we’ll break down the safe uses of Tylenol amoxicillin combinations, explain their role in common medical scenarios, and answer key questions like “can you take Tylenol with antibiotics” without risking side effects. By the end, you’ll feel confident about when to use Tylenol and amoxicillin—and when to consult your doctor.

Can You Take Amoxicillin and Tylenol Together?
Yes, you can safely take amoxicillin and Tylenol together in most cases. These two medications work in different ways—amoxicillin is an antibiotic that targets bacterial infections, while Tylenol (also known as acetaminophen) helps reduce pain and fever. Since their functions don’t overlap, doctors often recommend the combination of amoxicillin and Tylenol to manage both the source of infection and the discomfort that comes with it. Many patients are prescribed amoxicillin Tylenol especially when symptoms like sore throat, sinus pressure, or urinary discomfort are present.
The main difference between amoxicillin Tylenol is their classification and purpose: amoxicillin fights infection at its root, while Tylenol simply relieves symptoms like pain or fever. Taking both at the same time can be especially helpful when the infection is causing moderate to severe discomfort. For example, in cases of a dental infection or strep throat, using Tylenol amoxicillin helps the patient feel better while the antibiotic works to clear the bacteria.
Doctors often recommend tylenol amoxicillin for conditions such as urinary tract infections, ear infections, and dental abscesses. The combination of amoxicillin and Tylenol helps you heal while keeping pain under control, which can improve rest and recovery. Just be sure to follow the dosage instructions for both drugs. Whether your prescription reads amoxicillin Tylenol or your provider advises you verbally, this combination is widely accepted as both safe and effective in managing infections with pain.

III. Amoxicillin for Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
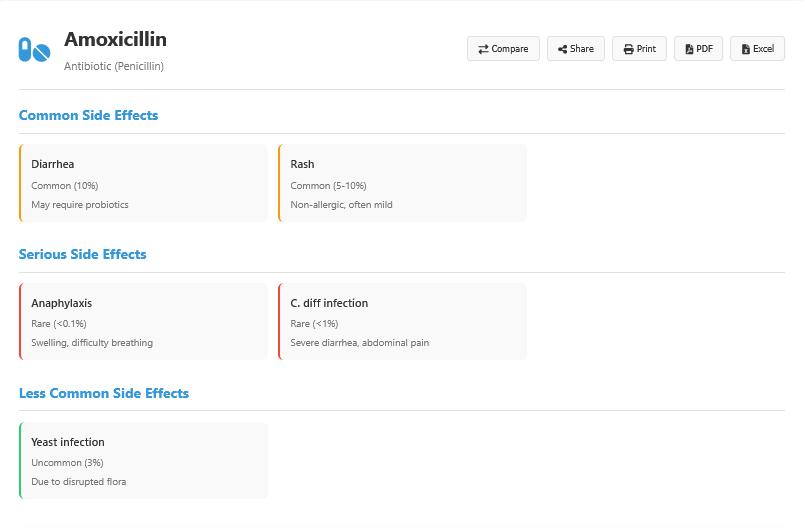
Amoxicillin is a commonly prescribed antibiotic used to treat various bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections. When a UTI is caused by bacteria susceptible to penicillin-type drugs, doctors often recommend amoxicillin for urinary tract infection due to its effectiveness and low side-effect profile. Patients who receive amoxicillin for UTI usually experience symptom relief within a few days, especially when the infection is caught early. The use of amoxicillin and urinary tract infection treatment is most effective when the full course of antibiotics is completed, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication.
However, amoxicillin for urinary tract infection is not always the first-line choice for all patients. In some cases, lab testing may show resistance to amoxicillin, requiring a switch to alternative antibiotics. Still, for many mild or uncomplicated cases, amoxicillin for UTI provides reliable results with fewer gastrointestinal side effects. It’s also important to note that amoxicillin and urinary tract infection treatment may be less effective if the infection involves the kidneys or if the patient has a history of recurring UTIs.
If amoxicillin for urinary tract infections isn’t effective or suitable, doctors may turn to alternatives such as urinary tract infection penicillin options or other antibiotics like nitrofurantoin or trimethoprim. These alternatives work in different ways and may be better suited depending on the bacterial strain involved. Still, amoxicillin for UTI remains a trusted option, especially in populations where broad resistance hasn’t developed. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting or stopping any antibiotic treatment for amoxicillin and urinary tract infection concerns.

IV. Using Tylenol for UTI Pain Relief
Tylenol is commonly used to manage the discomfort caused by urinary tract infections (UTIs), especially when antibiotics are still kicking in. UTI Tylenol combinations are recommended for reducing fever, body aches, and bladder pain while waiting for the infection to clear. While it doesn’t treat the root cause, UTI Tylenol is highly effective at controlling symptoms like burning urination and pelvic pressure. Many people rely on UTI Tylenol because it's accessible, fast-acting, and has minimal side effects when used correctly.
Understanding the safe dosage of Tylenol is crucial, especially when managing pain over multiple days. Adults should not exceed 3,000–4,000 mg of acetaminophen in a 24-hour period. For most UTI patients, 500 mg every 6 hours or 1,000 mg every 8 hours is considered a safe dosage of Tylenol—as long as no other acetaminophen-containing medications are taken simultaneously. Misuse can lead to liver damage, so sticking to a safe dosage of Tylenol is essential, particularly when using UTI Tylenol as part of a home treatment plan.
It’s important to note that UTI Tylenol is not a cure—it’s strictly for symptom relief. The infection still requires antibiotics like amoxicillin or other prescribed treatments. That said, for immediate comfort, UTI Tylenol plays a valuable role in improving quality of life during recovery. Always follow the safe dosage of Tylenol guidelines and consult your healthcare provider if symptoms persist or worsen. Using UTI Tylenol responsibly, while respecting the safe dosage of Tylenol, can make the painful waiting period more bearable.
V. Amoxicillin and Dental Pain: Is It Effective?
When you’re dealing with severe dental discomfort, it’s natural to look for fast relief. Many people wonder whether amoxicillin for a toothache is a reliable solution. In cases where an infection is present, a dentist might prescribe amoxicillin for a toothache to stop the bacterial growth causing the pain. However, while amoxicillin and toothache relief often go hand in hand, antibiotics alone won’t address the root cause of the problem, such as a cavity or abscess. It’s important to understand that using amoxicillin for a toothache is usually a temporary fix until proper dental treatment is provided.
Some people expect antibiotics like amoxicillin for a toothache to cure the issue entirely, but that’s a misconception. While amoxicillin and toothache treatment can reduce infection and swelling, it doesn’t eliminate the need for dental procedures such as fillings, root canals, or extractions. If you're experiencing intense discomfort, pairing amoxicillin for a toothache with an over-the-counter tylenol dental pain medication can offer temporary relief. In fact, many dentists recommend tylenol dental pain management to reduce inflammation and provide comfort while waiting for antibiotics to take effect.
For the best results, amoxicillin for a toothache should be used only under a dentist's supervision. Meanwhile, using a reliable pain reliever for dental pain, such as tylenol dental pain relief, can make a noticeable difference in managing symptoms. Whether you're dealing with amoxicillin and toothache side effects or simply need a pain reliever for dental pain, combining both approaches is often the most effective. Just remember, tylenol dental pain products address the pain but not the infection. Consult your dentist to determine if amoxicillin for a toothache is necessary alongside a trusted pain reliever for dental pain.
VI. Tylenol for Pain Relief: How Much is Too Much?
When it comes to managing everyday discomfort, Tylenol and pain relief go hand in hand. Known generically as pain acetaminophen, Tylenol is one of the most commonly used over-the-counter medications for headaches, muscle aches, and mild to moderate pain. But many people still ask, "Tylenol how much can you take safely?" Whether you're treating a toothache or a fever, understanding the proper use of pain acetaminophen is crucial to avoid accidental overdose.
The general dosage for adults is 500 to 1,000 mg every 4 to 6 hours, not exceeding 3,000 mg to 4,000 mg in a 24-hour period. However, the answer to "Tylenol how much can you take" depends on factors like your age, liver health, and other medications you're using. This is especially important when taking Tylenol extra strength Tylenol, which contains 500 mg per tablet. Overuse of pain acetaminophen can lead to serious liver damage, making it essential to stay within the safe range. If you're using other products that may also contain acetaminophen, add them to your total daily dose.
There’s also a difference between regular Tylenol and Tylenol extra strength Tylenol. While both offer Tylenol and pain relief, the extra strength version delivers a higher dose per tablet and is typically recommended for more intense pain. But remember, Tylenol how much can you take isn’t just about strength—it’s also about frequency and overall daily intake. Always read labels carefully and consult a doctor if you're unsure. Used properly, pain acetaminophen remains one of the safest ways to get fast and effective relief.
VII. Tylenol During Pregnancy: Is It Safe?
When expecting mothers experience headaches, mild fevers, or muscle aches, one common question arises: while pregnant can you take Tylenol safely? Tylenol, or acetaminophen, is often considered one of the safer over-the-counter pain relievers during pregnancy. Many healthcare providers recommend it when necessary, especially during the first and second trimesters, but it should always be taken under a doctor’s guidance.
Understanding the proper dosage is essential. While pregnant can you take Tylenol daily? The answer depends on the condition being treated and the duration. Typically, the maximum daily dose should not exceed 3,000 mg, and it’s best to use the lowest effective dose for the shortest possible time. If you're unsure, ask your OB-GYN, especially if you're dealing with chronic pain or recurring symptoms. Remember, while pregnant can you take Tylenol doesn’t mean it should be your first line of defense every time.
There are also some alternatives and precautions to consider. Natural remedies, rest, hydration, and prenatal-safe therapies may sometimes be more suitable. Additionally, avoid combining Tylenol with other medications that contain acetaminophen. Many women still wonder: while pregnant can you take Tylenol for sleep, stress, or back pain? The safest approach is always to check labels, limit self-medication, and consult your doctor. Your health and your baby’s development are worth the extra care. So the final takeaway? Yes, while pregnant can you take Tylenol, but only smartly, safely, and in moderation.
VIII. Summary & Precautions
Combining Tylenol (acetaminophen) with antibiotics like amoxicillin is generally considered safe for most people. While Tylenol helps reduce fever and relieve pain, amoxicillin works to fight bacterial infections. They target different symptoms, so using them together can be effective when managing conditions like dental infections, urinary tract infections, or sinus issues. However, understanding proper dosage and timing is crucial to avoid unnecessary side effects.
It's important to consult a healthcare provider before starting any new medication—especially if you're pregnant, taking other drugs, or managing chronic health conditions like liver disease or kidney issues. A doctor can confirm whether the combination is right for your specific case and may suggest alternatives if needed. Self-medicating without professional advice can lead to complications, particularly if symptoms persist or worsen.
To stay safe, always follow dosage guidelines for both Tylenol and antibiotics. Exceeding the recommended amount of acetaminophen can lead to liver damage, especially when combined with alcohol or taken over several days. Never double-dose if you miss a dose, and avoid mixing multiple medications that contain acetaminophen. Sticking to the prescribed amount and completing your antibiotic course helps ensure effective treatment and minimizes health risks.

IX. FAQs (SEO Schema-Enhanced Section)
Will amoxicillin cure a UTI completely?
Amoxicillin can be effective for treating urinary tract infections, especially when the bacteria causing the infection are sensitive to it. However, not all UTIs respond to amoxicillin, as some strains have developed resistance. It's essential to take the full prescribed dose and follow up with your doctor if symptoms persist.
Is it safe to take Tylenol with antibiotics like amoxicillin?
Yes, it is generally safe to take Tylenol (acetaminophen) alongside antibiotics such as amoxicillin. Tylenol can help reduce pain and fever while the antibiotic works to fight the infection. Always follow dosage instructions and consult a healthcare provider if you're on multiple medications.
Can I take Tylenol while pregnant for a toothache?
Tylenol is often considered the safest over-the-counter pain reliever during pregnancy. If you're experiencing a toothache while pregnant, Tylenol can help manage the discomfort. However, it's best to use the lowest effective dose and consult your OB-GYN before starting any medication during pregnancy.
What painkiller works best for a dental infection?
For mild to moderate dental pain, acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen are commonly recommended. Ibuprofen may offer additional anti-inflammatory benefits, but Tylenol is a suitable alternative for those who cannot take NSAIDs. In cases of infection, pain relievers are typically used alongside antibiotics like amoxicillin.
What’s the max dosage of Tylenol in a day?
The maximum recommended daily dose of Tylenol for adults is 4,000 mg. However, it's safer to stay under 3,000 mg per day to avoid liver damage. Always read the label carefully, and avoid combining multiple medications that contain acetaminophen.